Within an increasingly competitive economy, modern companies need to be able to respond quickly to their customers’ desires.
When we talk about companies where technology is a differentiating factor, agility becomes even more important.
Thus, having a software architecture that allows the company to react to the market with agility, is essential.
The architecture of software describes how the different elements of an application will be arranged and how they interact with each other.
This marks as one of the first steps in software development and occurs during the design phase. It is usually done by a software architect or solution architect, a central element of the development project.
In the software development world, there are some well-known architectures, but the focus of this blog will be on only two of them, namely, Model-View-Controller (MVC) Standard and Microservices.
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern is a way of breaking an application or to precisely separate the logic of the code, into three parts: the model, the view, and the controller
Model: This part manages the data on your site. Its role is to retrieve the raw information from the database, organize, and assemble it so that it can be processed by the controller.
View: This part focuses on the display. It is here that the data recovered by the model will be used to present them to the user.
Controller: This part manages the logic of the code that makes decisions. When the user interacts with the view, the request is processed by the controller.
It waits for the user to interact with the view to retrieve the request. Thus, it is the controller that will define the display logic, and display the next view on the screen.
Also Read: What is MVC? : MVC vs MVP
Microservices can be defined as an improvement, a kind of refinement, of what we know as service-oriented architecture (SOA).
In this architecture, a large application is made in the form of small monofunctional modules. Each microservice is autonomous.
Microservices do not share a data layer. Each has its own database and load balancer. So that each of these services can be deployed, adjusted, and redeployed individually without jeopardizing the integrity of an application.
As a result, you will only need to change one or more separate services instead of having to redeploy entire applications.
Also Read: Microservices vs. API: Know the Difference
• Both have a decoupled architecture.
• Their components can be worked upon independently helping with throughput time.
MVC: Division across three code components only Model, View, and Controller. This model is being used by companies like Microsoft, Dell, and Marketwatch.
Microservices: An app is divided into a set of specialized which are not predefined like that in MVC and interact with each other using APIs. This model is being used by companies like Netflix, Spotify, and eBay.
The segregation of development is easier in microservices since the development team can divide the coding part as per their choice. But in the case of MVC, it is restricted to three units only.
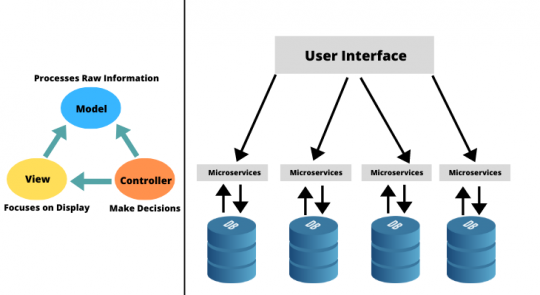
MVC Architecture (left) and Microservices Architecture (Right)
With the increasing complexity of systems/sites developed today, this architecture is focused on dividing one big problem into several smaller and less complex ones.
Thus, any kind of changes in any one of the layers does not interfere with others, making it easier to update layouts, change business rules, and add new features.
For large projects, MVC greatly facilitates the division of tasks among the team.
Listed below are some of the benefits of using MVC in your projects:
- Easy maintenance and addition of features.
- Reduces project development time.
- Helps build reliable software with tested architectures.
- Facilitates code reuse.
- Greater team integration and division of tasks.
- Reduced complexity in code.
Unlike traditional monolithic architecture, microservice architecture is an approach in which the application is structured through several small standalone services that work together.
Today, with cloud platforms like AWS and AZURE, we can build Microservice architectures much more quickly, with native services that are self-managed or Serverless, for example, EC2, ALB, ECS, EKS, FARGATE, and several others.
Listed below are some of the benefits of using microservices in your projects:
- Makes continuous and automated deployment possible.
- Allows developers to make appropriate and service-specific decisions.
- Each microservice has its own database.
- Enables companies to optimize resources for development and applications.
- Optimizes sizing and easy to integrate with third-party services.
You may also like to read:
Microservices vs. Web Services: How the two Software Development Architecture Differ?
Docker vs. Virtual Machine: Understand the Difference between the Two